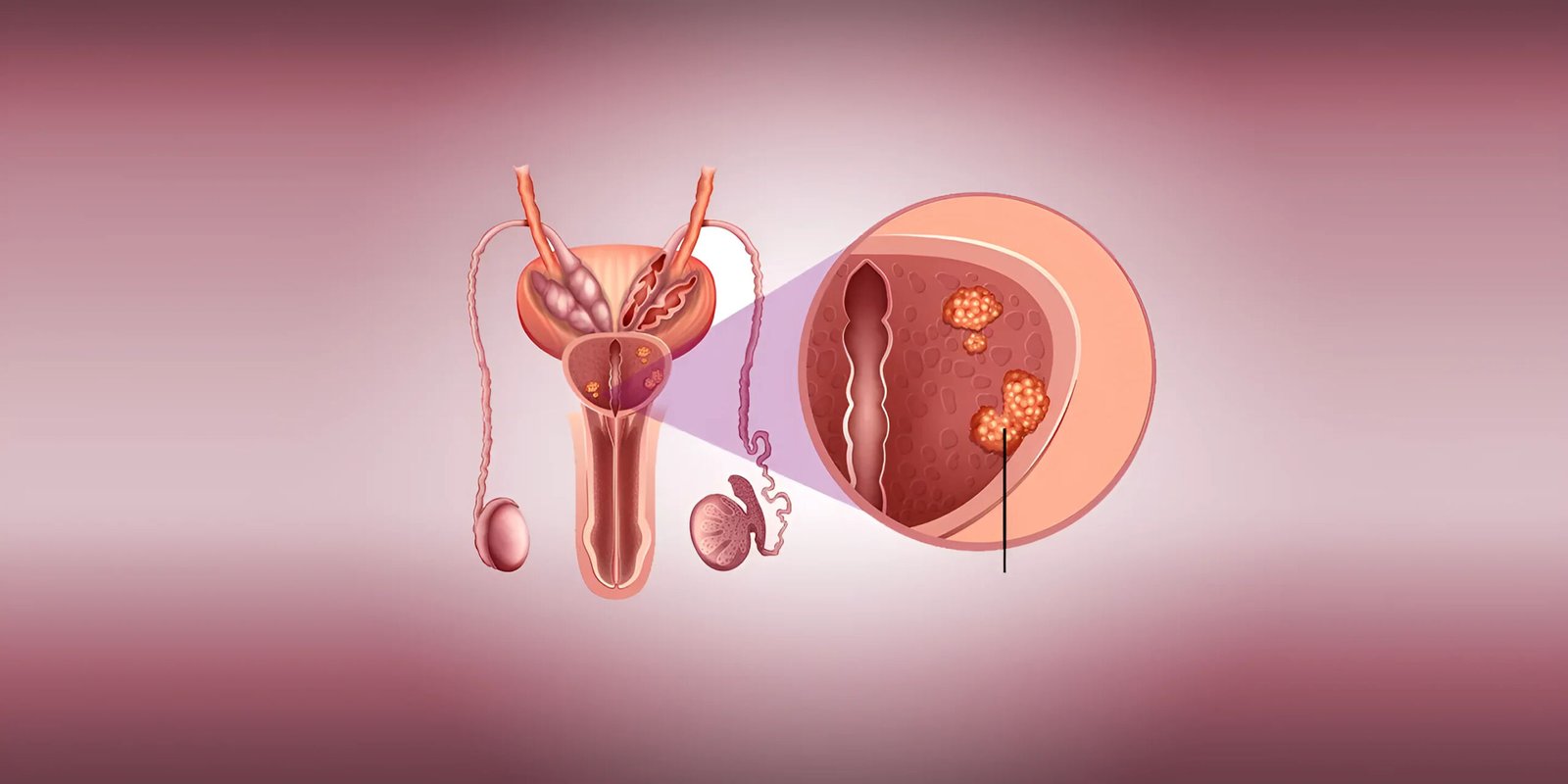
Prostate cancer is a common form of cancer that arises from the prostate, a small gland located below the bladder in men. The prostate’s primary function is to produce seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Although prostate cancer often progresses slowly and may not cause immediate harm, it is crucial to be aware of its potential impact on health.
Recognizing and understanding the symptoms of prostate cancer is paramount to early detection and effective treatment. As with many cancers, early detection significantly improves the chances of successful intervention and recovery. This article will discuss the various symptoms associated with prostate cancer, providing information necessary for individuals to monitor their health and seek timely treatment if necessary. With awareness and understanding of these symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps toward their wellness and potentially improve their outcomes in the face of prostate cancer.
Symptoms
A. Frequent urination
Frequent urination is a common symptom associated with prostate cancer. Men experiencing these symptoms may need to urinate more often than usual, especially at night. While other conditions, such as urinary tract infections, can also cause frequent urination, persistent changes in urination habits should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out possible prostate problems.
B. Impaired or Obstructed Urine Flow
A weak or interrupted urine flow is another significant symptom of prostate cancer. As the prostate gland enlarges, it can put pressure on the urethra, making it difficult to maintain a steady and vigorous flow of urine. This can lead to a feeling of incompleteness after urination, and the problem can gradually worsen over time.
C. Straining During Urination
Straining during urination is often associated with urethral obstruction due to an enlarged prostate. Men with prostate cancer may need to exert extra effort to initiate or complete urination. This symptom indicates a possible prostate-related concern and requires medical attention for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
It should be recognized that these urinary changes can also be attributed to non-cancerous conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Nevertheless, any persistent change in urinary pattern should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and appropriate action. Regular screening, especially for at-risk individuals, can contribute to early detection of prostate cancer and increase the chances of successful treatment.
D. Hematuria (blood in urine)
The presence of blood in the urine, medically known as hematuria, can be a symptom associated with prostate cancer. Although hematuria can also result from other conditions such as urinary tract infections or kidney stones, it should not be ignored, and medical attention should be sought. In the context of prostate cancer, blood in the urine may indicate potential problems with the prostate gland and require further evaluation to determine the underlying cause.
E. Presence Of Blood In Semen
Another significant symptom associated with prostate cancer is the presence of blood in the semen, a condition known as hematospermia. This phenomenon may be alarming and individuals should be urged to seek immediate medical advice. Although prostate cancer is a possible cause, hematospermia can also be caused by infection, inflammation, or other non-cancerous conditions. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough examination and diagnostic tests to identify the cause and initiate appropriate treatment.
Both hematuria and hematospermia are symptoms that require careful evaluation by a healthcare provider. It is important to note that these symptoms can have various origins and a comprehensive medical evaluation is crucial to determine the underlying cause and ensure appropriate intervention. People experiencing such symptoms should not delay in seeking medical help to facilitate timely diagnosis and management.
F. Discomfort or Pain In The Pelvic Area
Pelvic discomfort or pain is a possible symptom associated with prostate cancer. Men with prostate cancer may experience a persistent, vague discomfort or pain in the pelvic area. This discomfort can range from mild to more pronounced and its presence should be brought to the attention of a healthcare professional for further evaluation. Pelvic discomfort can be caused by prostate enlargement or the spread of cancer cells to nearby tissues.
G. Pain In The Perineum, Anus, or Lower Back
In addition to pelvic discomfort, prostate cancer can manifest with pain in specific areas such as the perineum, anus, or lower back. The perineum is the area between the testicles and the anus, and pain in this area can signal prostate-related problems. Pain in the anus or lower back may occur as the cancer progresses or spreads to surrounding tissues and bones.
It is extremely important to consult a health care provider immediately for people experiencing pelvic discomfort or localized pain in the perineum, anus, or lower back. These symptoms can be indicative of a variety of conditions, including prostate cancer, and a thorough examination in addition to diagnostic tests is necessary to determine the cause. Early detection and intervention are key to effectively managing prostate cancer, and seeking medical help for persistent discomfort or pain is an important step in the process.
H. Difficulty Achieving an erection
Erectile dysfunction (ED) refers to difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection sufficient for sexual activity. Although ED can have a variety of causes, it is cited as a potential symptom associated with prostate cancer. The prostate’s proximity to nerves and blood vessels crucial to erectile function makes it susceptible to changes caused by prostate cancer or its treatment. Men with persistent problems with erections should consult a healthcare professional to explore possible underlying causes related to prostate health.
The relationship between erectile dysfunction and prostate cancer often stems from the effects of the cancer or its treatment on the nerves and blood vessels in the pelvic region. Prostate cancer treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy, or hormone therapy can affect the delicate balance needed for normal erectile function. Addressing concerns about erectile dysfunction with a healthcare provider is essential, as it can provide insight into potential prostate health issues and guide appropriate interventions.
I. Bone Metastasis
In advanced stages of prostate cancer, cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body, a process known as metastasis. Bone metastasis is a common occurrence in advanced prostate cancer, where cancer cells travel to and settle in the bone. This can lead to bone pain and other complications.
J. Potential Pain (hips, spine, pelvis)
Bone pain associated with prostate cancer metastasis often manifests in specific areas, including the hips, spine, and pelvis. Pain in this area can be an indication of cancer affecting the bone, causing discomfort that can range from aching to severe pain. Understanding the potential locations of bone pain can help individuals and healthcare professionals identify and address issues related to advanced prostate cancer.
It is important to recognize that symptoms associated with prostate problems can be caused by non-cancerous conditions. Conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, or urinary tract infection can share symptoms such as changes in urination patterns, pelvic discomfort, or blood in the urine. It is very important to understand that these symptoms may not exclusively indicate prostate cancer. An accurate diagnosis requires a physician’s consultation, allowing healthcare professionals to distinguish between cancerous and non-cancerous conditions and recommend appropriate management.
The importance of seeking medical advice for persistent or related symptoms cannot be overstated. Whether symptoms are attributed to a cancerous or non-cancerous condition, prompt consultation with a healthcare professional ensures a thorough evaluation. Early detection and intervention greatly impact treatment outcomes, and men experiencing symptoms related to prostate health should not hesitate to seek medical help. Professional guidance helps in proper diagnosis, proper management, and initiation of appropriate treatment plan if needed.
Screening and Early detection
Routine screening plays an important role in the early detection of prostate cancer. A prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test measures the level of a protein produced by the prostate, with high levels indicating potential problems. Digital rectal examination (DRE) involves a physical examination to evaluate the size, shape, and texture of the prostate. Regular screening provides healthcare professionals with the information they need to detect potential abnormalities at an early stage.
Age and family history are very important to consider in determining the risk of prostate cancer. Regular screening is often recommended for men age 50 and older, as well as those with a family history of prostate cancer. However, discussions with health care providers can lead to personalized screening plans based on individual risk factors and health history.
Before screening, discussion of benefits and risks with health care providers is essential. While screenings aid in early detection, they can also lead to false positives, which can lead to unnecessary anxiety and potentially invasive follow-up procedures. Understanding the benefits and risks of screening allows individuals to make informed decisions about their health care. Open communication with health care providers ensures that screening plans are tailored to individual needs and preferences.
In summary, considering non-cancerous conditions, seeking prompt medical advice for symptoms, and engaging in regular screening are integral components of prostate health awareness. These actions potentially contribute to early detection, personalized care and improved outcomes for men affected by prostate cancer.
Conclusion
The importance of early detection of prostate health cannot be overstated. Prostate cancer, like many cancers, often exhibits subtle symptoms in its early stages. Promptly identifying and addressing these symptoms can lead to more effective treatment outcomes and potentially improved quality of life. Regular screening and proactive health care practices play an important role in identifying potential problems before they progress. Embracing the importance of early detection encourages individuals to take charge of their health, a proactive approach to managing and preventing prostate-related concerns.
Encouraging individuals to seek treatment for any symptoms is a key message in promoting prostate health. Whether experiencing changes in urination patterns, pelvic discomfort, blood or semen in the urine, or other symptoms related to prostate problems, it is imperative to consult a healthcare professional. Timely medical consultation allows for a thorough assessment, accurate diagnosis and initiation of appropriate interventions. Active involvement in one’s health not only contributes to early detection but also increases the likelihood of successful outcomes in managing prostate health conditions.
In conclusion, raising awareness, advocating for routine screening, and promptly addressing symptoms are important in maintaining prostate health. By emphasizing the importance of early detection and encouraging a proactive approach to seeking medical attention, individuals can play an active role in their well-being and contribute to the effective management of prostate-related problems. Regular discussions with health care providers, adherence to recommended screenings, and a commitment to overall health form the foundation for a proactive and informed approach to prostate health.