Introduction:
There are few common Hair transplant side effects those will discuss here in this article. Hair transplant Hair transplant procedures have become increasingly popular in recent years as a permanent solution to hair loss. While these treatments offer promising results, it’s essential for individuals considering hair transplantation to be well-informed about potential side effects. In this article, we’ll delve into the common side effects associated with hair transplants, providing a comprehensive overview to help you make an informed decision.
Common Side Effects Of Hair Transplant
1. Temporary Swelling and Redness:
Swelling is a common side effect after a hair transplant procedure, particularly around the forehead and the eyes. It is usually temporary and subsides within a few days or weeks. After a hair transplant, it’s normal to experience some swelling and redness on the scalp. This is a common side effect resulting from the trauma the scalp undergoes during the procedure. However, these effects are temporary and typically subside within a few days to a week. Applying cold compresses and following post-operative care instructions can help alleviate discomfort

2. Pain and Discomfort:
Some individuals may experience mild pain or discomfort at the donor and recipient sites. This can be managed with prescribed pain medications and typically resolves within a few days.
3. Itching and Numbness:
Some individuals may experience itching in the transplanted area during the healing process. This is a normal part of the body’s response to the healing process. Numbness in the donor and recipient areas can also occur but is usually temporary, resolving as the nerves regenerate over time.
Itching in the donor or recipient area is common during the healing process. It is important to avoid scratching or picking at the transplanted area to prevent any damage or infection.
4. Infection:
Although rare, there is a slight risk of infection after a hair transplant. Proper post-operative care, including keeping the area clean and following the surgeon’s instructions, can significantly minimize this risk.
5. Bleeding:
Minimal bleeding may occur during or after the procedure. The surgeon will take necessary precautions to control bleeding during the surgery, and any post-operative bleeding can usually be managed with gentle pressure and dressing changes.
6. Infection and Scarring:
While rare, infection is a potential risk associated with any surgical procedure, including hair transplants. Following proper post-operative care instructions, including keeping the scalp clean and avoiding scratching, can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Additionally, modern transplant techniques aim to minimize scarring, but some scarring is inevitable. Most scarring is discreet and easily concealable under existing hair.
Hair transplant procedures typically leave small scars in the donor area, which are usually concealed by surrounding hair. In some cases, visible scarring or keloid formation may occur, but this is rare.
7. Shock Loss:
Shock loss refers to the temporary shedding of existing hair around the transplant site. This is a normal part of the hair transplant process and usually resolves within a few months as new hair starts to grow.
8. Numbness or Tingling:
Some individuals may experience temporary numbness or tingling in the scalp, which is generally a result of nerve irritation during the procedure. This sensation typically resolves on its own over time.
It is important to note that the severity and occurrence of these side effects can vary from person to person. Choosing a skilled and experienced surgeon, following post-operative instructions diligently, and maintaining good overall health can help minimize the risks associated with hair transplant surgery.
9. Unnatural Looking:
Sometimes, individuals may be dissatisfied with the aesthetic outcome of their hair transplant. This can be due to a variety of factors, including poor surgical technique or unrealistic expectations. Choosing a reputable and experienced surgeon is crucial to achieving natural-looking results. Consultations prior to the procedure can help set realistic expectations and address any concerns.
10. Cysts:
Small cysts may develop at the transplant site, but these are usually benign and resolve on their own. In rare cases, they may need to be drained by a medical professional.
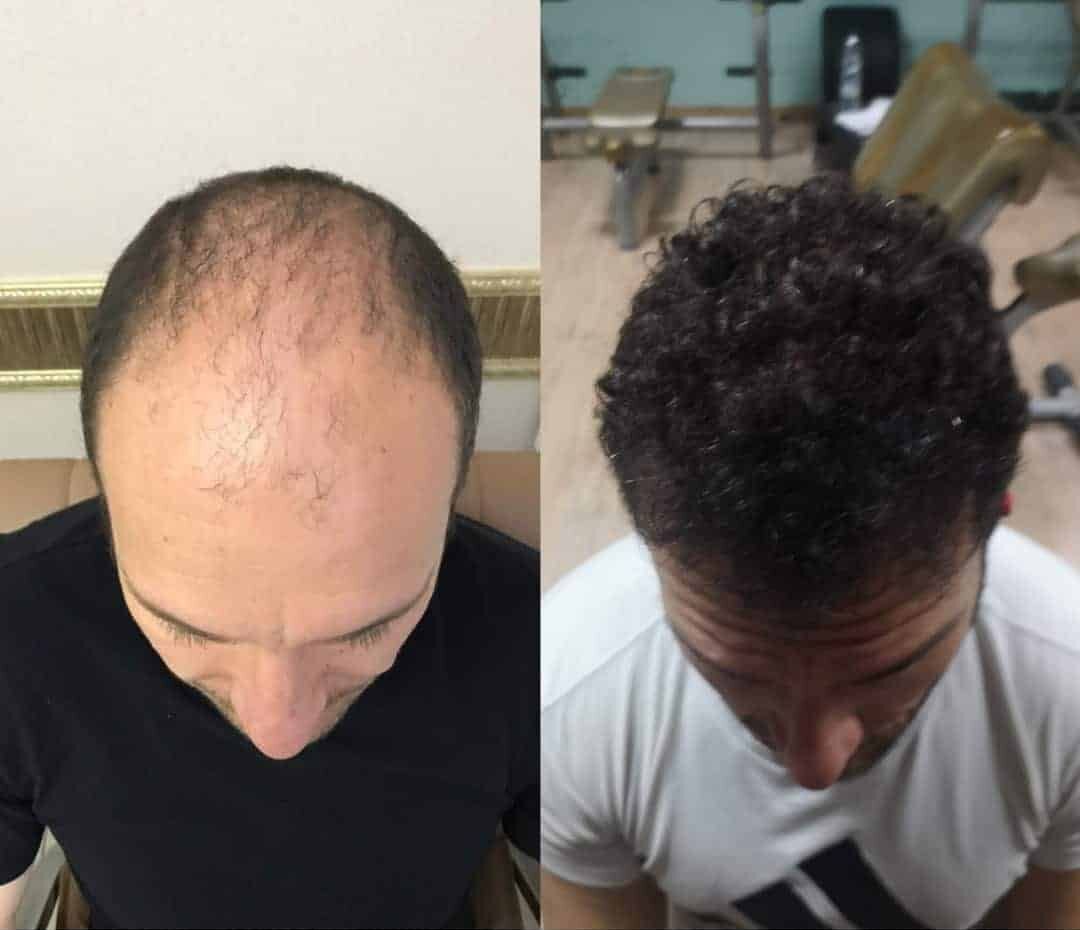
Hair loss can have a profound impact on an individual’s confidence and self-esteem. For those seeking a lasting solution, a hair transplant can be a game-changer. In this article, we will explore the remarkable transformations that individuals undergo through hair transplant procedures by examining compelling before-and-after stories.
Hair Transplant Before and After
Many individuals facing hair loss often find themselves trying various remedies, from over-the-counter treatments to unconventional methods. However, for some, these solutions fall short, leaving them feeling frustrated and self-conscious about their appearance. Before opting for a hair transplant, people may experience thinning hair, receding hairlines, or even bald patches, affecting their overall confidence.
After: The Impact of a Hair Transplant
The decision to undergo a hair transplant is a significant step toward regaining confidence and a more youthful appearance. The procedure involves transplanting hair follicles from donor areas to areas with hair loss. As the transplanted hair grows naturally, the results become increasingly evident.
1. Natural-Looking Hair Growth:
One of the most remarkable aspects of a successful hair transplant is the natural-looking growth of transplanted hair. Skilled surgeons meticulously place grafts to mimic the natural direction and pattern of hair growth, ensuring seamless integration with existing hair.
2. Restored Hairline:
For those with receding hairlines, a hair transplant can restore a more youthful and balanced appearance. Surgeons carefully design the new hairline to complement facial features, creating a harmonious and aesthetically pleasing result.
3. Increased Density:
Individuals experiencing thinning hair often see a significant increase in hair density after a transplant. This enhanced fullness contributes to a more voluminous and youthful hairstyle.
4. Boosted Confidence:
Perhaps the most rewarding aspect of a successful hair transplant is the boost in confidence and self-esteem. Many individuals report feeling more comfortable in social situations and expressing a renewed sense of self-assurance after regaining their natural-looking hair.
Before and After Images:
To truly appreciate the impact of a hair transplant, viewing before-and-after images is invaluable. These images showcase the journey from hair loss to restored confidence, providing a visual representation of the transformative effects of the procedure.
Conclusion:
While hair transplant procedures offer a long-term solution to hair loss, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects. Choosing a skilled and experienced surgeon, following post-operative care instructions, and maintaining realistic expectations can significantly minimize the risk of adverse effects. As with any medical procedure, individuals considering a hair transplant should consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine if it’s the right option for them.
If you experience any persistent or concerning side effects after a hair transplant, it is crucial to contact your surgeon for further evaluation and guidance.
A hair transplant can be a life-changing experience for individuals struggling with hair loss. The remarkable transformations seen in before-and-after stories underscore the effectiveness of this procedure in restoring not just hair but also confidence and self-esteem. As with any medical decision, thorough research and consultation with a qualified professional are crucial steps for those considering a hair transplant to ensure realistic expectations and optimal results.
















